In June 2018, Google rebranded Google AdWords and changed it to Google Ads. If you have been using the platform for your PPC ads, you may have been transitioned to the new interface.
The improved user experience and features are designed to help small businesses advertise on Google’s network more effectively.
While these new changes will make it easier to create, manage and optimize your ads, there is also a learning curve when you adjust to the new tools.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll show you everything you need to know to get the most out of the new Google Ads platform. You’ll learn the inner workings of PPC campaigns, the different campaign types and ad options, account structure and landing page best practices, as well as reporting and analysis.
Ready to optimize your Google Ads for higher ROI? Let’s go…
Meet the New Google Ads
The new interface, which is faster and more user-friendly, unifies the access to both Google Search Network and Google Display Network (GDN). It also comes with some new tools and features to help advertisers optimize results:
- Life event targeting on YouTube and Gmail Ads.
- Ability to target prospects who are ready to make a purchase on the search network.
- Location extension for YouTube ads.
- Ability to solicit feedback from customers using Google Survey 360.
- Google Attribution to track the impact of a campaign across channels.
- AMP ads and landing pages for a better mobile user experience.
- Google Optimize to streamline landing page testing.
- New landing page report and page speed tool to help optimize the mobile experience.
- The inclusion of Google Assistance, which integrates mobile search with offline shopping experiences.
How Google Ads PPC Works
To optimize the results for your Google Ads, you need to understand how the key components of this PPC (pay-per-click) system work.
Auction Process
The auction process happens with each Google search. It determines which ads and in what order they appear on the search results page.
Every time someone enters a search term into Google, the system finds all the keywords that match the search. Among the ads, the system ignores those that aren’t eligible (e.g., targeting a different country.)
The system will then determine the Ad Rank of the remaining ads. Ad Rank is a function of your ad bid and the quality score:

Since the position of an ad is determined by a combination of factors other than the bid, you can win a higher position at a lower price if you dial in all the other aspects that affect your quality score.
The auction process happens on every search, and your ranking is likely to fluctuate, depending on the competition at the moment.
Quality Score
Since your quality score can have a significant impact on your cost-per-click (CPC) and ad ranking, let’s take a closer look at this important component of the equation.
The quality score reflects the quality of your ads, their relevance to the keywords and the user experience of the landing pages. It’s an aggregated estimate of your overall performance in ad auctions, and you can see yours by going to the keywords’ “Status” column on your dashboard.
Your quality score is determined by:
- Your click-through-rate (CTR).
- Each keyword’s relevance to its ad group.
- The quality and relevance of your landing pages.
- Your ad text’s relevance.
- The past performance of your Google Ads account.
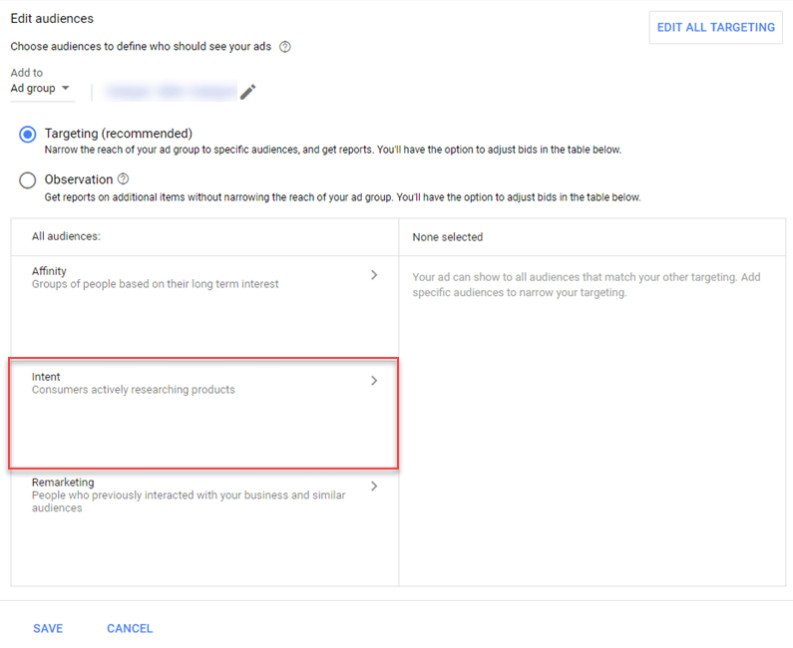
User Intent
The introduction of the custom intent audience feature allows GDN’s advertisers to take customer lifecycle stages into account when targeting their ads.
This tool makes it possible for you to reach a custom audience that’s more likely to buy the product or service you’re advertising in the foreseeable future (i.e., they have a higher purchase intent).
By targeting an audience who’s most likely to be interested in your products and click through your ads, you’re increasing your CTR, improving your quality score and lowering your CPC.
You can either build your own custom intent audience manually or let Google’s machine learning algorithm do it for you. Simply go to the “audience” interface on your dashboard, select the “targeting” radio button and choose “intent.”
Google Ads Campaign Types
There are different types of Google Ads campaigns, and choosing the right kind can help you get the most of your ad dollars. Here’s an overview:
Google Search Network
Running ads on the Google Search Network is probably the most common and well-known form of PPC advertising.
When you use this network selection, your ads will appear on Google SERPs (search engine results pages). You can expand your reach by extending the targeting to include “search partners,” which will show your ads on the SERPs of other search engines in the network (e.g., AOL).
This type of campaign is very effective because it targets active searchers who are looking for the exact products or services you’re offering. In addition, it’s highly measurable so you can quantify the ROI easily.
This campaign type is particularly suitable for advertisers who have a limited ad budget and/or offer a product or service that consumers look for on an “as-needed” basis (e.g., plumbers, locksmiths, electricians, etc.) because the ads will appear exactly when a searcher is in need of the products or services.
Google Display Network (GDN)
This campaign type allows you to place ads on a collection of over two million websites (e.g., blogs, news sites, YouTube) that are in the Google Display Network, giving you the ability to reach more than 90 percent of all global Internet users.
The campaign is most effective for building brand awareness, increasing visibility and broadening your reach. You may also see an uptick in clicks on organic search listings or brand-specific searches after running this type of campaign for a while.
If you have a lengthy sales process (e.g., luxury products) that benefits from being top-of-mind or utilizing remarketing to move customers through the sales funnel, GDN ads can be particularly useful.
In addition, if you have a “sexy” product (i.e., looks good on photos) or compelling video collaterals, GDN ads can help capture the attention of your audience and drive more traffic.
To increase the effectiveness of your ads, use the right targeting options so they’re shown on sites most frequented by your ideal customers. Also, keep in mind that GDN ads typically have a lower CTR than Search Network ads so make sure to segment your campaigns accordingly for your analytics.

Search Network with Display Select (SNDS)
You can think of SNDS as a hybrid between Search Network and Display Network campaign.
When you run an SNDS campaign, your ads are matched to publisher sites across the GDN based on a series of criteria, such as purchase intent and keywords, so they’re displayed alongside the most relevant content.
This campaign type has helped advertisers increase the reach of their campaigns, boost click-through-rates and reduce cost-per-conversion when compared to search or display campaigns.
However, you’ll be giving up significant control of your campaign over to Google. If you want more granular control, you still need to manage your search and display campaigns separately.
Google Shopping
These product-listing ads are prominently placed at the top of the SERPs above text ads and organic search results. They’re shown to users who are looking for a specific product and have high purchase intent. As a result, they typically lead to higher CTRs and conversion rates.
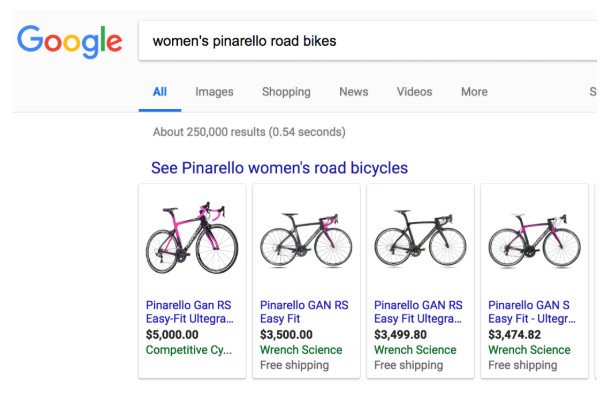
Google Shopping ads are great for targeting long-tail keywords so you can rank for search terms that are less competitive, less expensive and better converting.
Here’s how you can optimize a Google Shopping ad campaign to increase CTR and conversion rates:
- Create multiple ad sets to target potential customers at various stages of the buyer’s journey.
- Use enticing product images to capture attention.
- Optimize the product title, description and pricing.
- Segment your products by product ID to get more granular with your optimization strategy.
- Test and fine-tune your bids constantly.
Google Ads Options
All the tabs and dropdowns on the Google Ads dashboard can be quite overwhelming. Understanding these options is essential to setting up your campaigns correctly so you can maximize your ROI.
Targeting
You can set your targeting based on the user’s device and location:
Device Targeting
Set at the campaign level, device targeting allows you to choose what device(s) to display your ads. For example, you can use device-specific content or features to drive more engagement and conversion.
- Computers: desktop or laptop devices with screens larger than 7″ in diagonal.
- Mobile: handheld devices that include a smartphone. Types of mobile ad spaces include mobile app, mobile app interstitial and mobile web.
- Tablet: mobile devices that don’t include a phone. Types of tablet ad spaces include tablet app, tablet app interstitial and tablet web.
- TV screens: devices that stream TV content, such as smart TVs, gaming consoles and connected devices (e.g., Chromecast). You can only use this option for Display and Video campaigns.
Location Targeting
Location targeting is particularly useful if you run a local business or only ship to selected regions. This will make sure your ads aren’t shown to people who won’t be able to purchase from you.
There are different types of location targeting options:
- Physical location: targeting based on the searcher’s IP address or device-based location signal. You can adjust the radius of each location to fine-tune the targeting.
- Search intent: Did you know that there are 33 places named Springfield in the U.S.? How can you make sure your ad is served to people in the right location? Sometimes you need to give Google a little help by adding search intent to the criteria, such as location terms in users’ queries or context from previous searches.
- Physical location or search intent: You can target searches that match criteria based on either physical location or search intent to maximize your reach.
Keep in mind that advanced location targeting is only available for the Search Network and doesn’t work on GDN (yet).
Scheduling
If you look at your analytics, you may notice that your ads perform better during certain days of the week and certain times of the day. For example, most B2B companies get the best CPA (cost-per-acquisition) during working hours.

Why not focus more of your budget on those times so you can maximize your ROI?
With Google Ads’ scheduling (dayparting) option, you can get more visibility during the times when your target audience tends to look for the products or services you offer.
Not every advertiser can benefit from scheduling. For many B2C brands, the CPA is often quite leveled throughout the day so they don’t have to spend the time and resources on managing this option.
Here’s how to get the most with Google Ad scheduling:
- Review your data to see if there’s any trend in the ad performance that relates to the day of the week or the time of the day.
- Start with the data of your highest performing campaigns over a statistically significant time period.
- If you can identify a clear common trend, then fine-tune your campaigns by creating a schedule that focuses on the top-performing days and times.
- Don’t forget to revisit the performance of your campaigns regularly to see if the new schedule is improving the key metrics.
Budget
We can’t really talk about advertising without looking at your budget and how to maximize its return.
On your Google Ads dashboard, you can set an average daily budget for each campaign and change it any time. This number represents the average amount you want to spend per day over the course of a month, and daily spending may vary.
You can also set a total budget for video campaigns with a specific start and end date.
Here are a few things to keep in mind when setting your Google Ads budget:
- Understand how Google Ads fit into your overall marketing strategy so you can allocate your funds properly.
- Find out how much and on what keywords your competitors are spending.
- Know exactly what the CPC is for the keywords you’re bidding on.
- Measure the right KPIs that correspond to your business objectives.
- Strategically allocate the ad spend to support your marketing objectives. For most advertisers, the majority of the budget should be focused on the highest-converting keywords.
- Distribute your budget across different campaign types (e.g., search network, display network, shopping, remarketing, etc.).
Delivery Method
Closely related to budget is your delivery method, which affects how long your budget will last.
“Standard” delivery will evenly distribute your budget throughout the day so it won’t get exhausted too quickly. This is recommended for new advertisers because you can see how your campaigns perform throughout the course of the day so you can get the necessary data to fine-tune the scheduling.
“Accelerated” delivery will use up your budget more quickly, typically during the early part of the day. Even though it’s not recommended for most advertisers, it may benefit a campaign if you need to show your ads to as many people as early as possible.
In addition, accelerated delivery can be helpful if you haven’t been using up your daily budget. Your ads will be entered into all eligible auctions and increase the chances of getting more clicks.
Ad Rotation
By creating multiple ads in an ad group, you can rotate them to find out what works best in your market.
The “optimize” option uses Google’s machine learning technology to deliver ads that are expected to perform best based on signals such as keyword, search term, device, location and more.
The “rotate indefinitely” option will put the ads in an ad group to be delivered more evenly. However, it won’t favor better performing ads nor will it automatically optimize your campaigns.
For most advertisers, Google recommends choosing the “optimize” option. In one study, the “optimize” option yields an 8 percent increase in CTR and 11 percent increase in CVR for over 400 accounts.
Google Ads Account Structure
Your account structure is how you organize the various pieces of your Google Ads account, from keyword-level all the way up to campaign level.
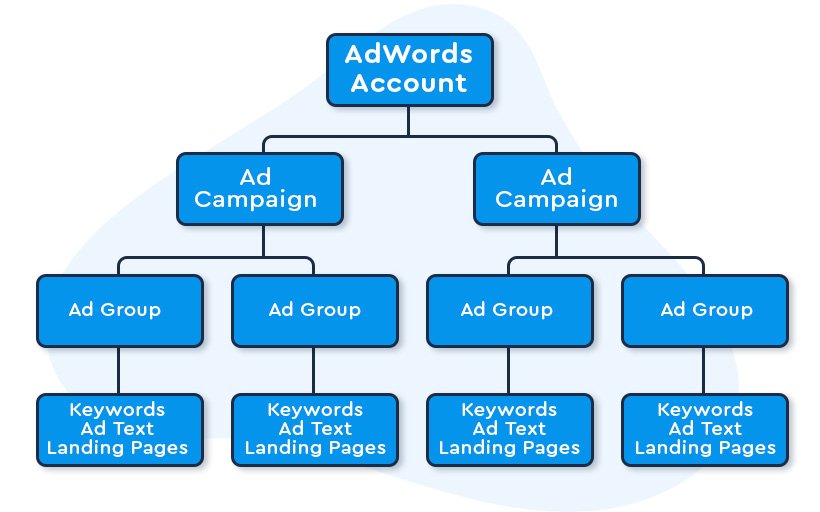
Here are some key components and what you should know about them:
Keywords
Keywords are the foundation of any PPC campaign and knowing what to look for can help you get the most out of your ad dollars.
Keyword Research
Your ability to rank for the right keywords can make or break a campaign. Here are a few latest and greatest tips on keyword research:
- Use synonyms and related words or phrases to take advantage of Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI).
- Speak your audience’s language and use keywords that resonate with your target market.
- Use a keyword generator, such as Google’s Keyword Tool, dictionary.com and thesarus.com to compile a keyword list.
- Use questions as your key phrases will provide Google with context and increase the likelihood that your ad will be shown to users who type similar questions into the search box (which is becoming increasingly common).
- Find out what pages are getting ranked for certain keywords and the metadata associated with each high-ranking web page.
You should build out your account to ensure the coverage of as many relevant keywords as possible.
Match Type
When you bid on a keyword, you need to tell Google how aggressively or restrictively you want the queries to match the keywords by selecting a keyword match type for each campaign.
- Broad match: It’s the default match type that will reach the widest audience. It covers queries that include misspellings, synonyms, related searches and other relevant variations.
- Negative keywords: This will exclude your ads from showing up in searches that include the specified keywords. This feature is particularly useful if your ads are being shown on queries related to a specific keyword but aren’t generating sales.
- Phrase match: Ads set to this match type will be shown to queries containing a key phrase that uses keywords in the exact order you have specified. Note that the queries may contain additional words before or after the phrase.
- Exact match: This is the most restrictive match type as users can only see your ads if they type in the exact keywords or phrases that you specified.
- Modified broad match: This is a hybrid between broad match and phrase/exact match. You can adjust the parameter by “locking” individual words in a key phrase.
Dialing in your keyword match type is important to get your ads shown to the right audience.
Search Volume
The search volume associated with each keyword tells you how many searches are performed against a certain keyword within a specific time frame.
When you target keywords with very high search volume, you’re likely to be competing with larger sites, and it will be more difficult to rank high in the search results. On the other hand, if you target keywords with very low search volume, you may not reach a large enough audience.

Balance search volume with competition by taking a variety of factors into account, e.g., your domain authority — the higher your domain authority, the more likely you’ll get ranked for competitive keywords with high search volume.
Campaigns
You can select different campaign types to display your ads in the right places so you can achieve your marketing objectives:
- Search network only: reach potential customers with high purchase intent looking for the exact products or services you offer.
- Display network only: build brand awareness and increase visibility.
- Call only: generate phone calls to your business.
- Remarketing: re-engage previous visitors or past customers.
If you have different advertising goals, you should set up corresponding campaigns to optimize the effectiveness of your ads.
Since you’ll be setting up your budget at the campaign level, structure your campaign topics according to how you want to distribute your budget.
Ad Groups
You can create multiple ad groups under each campaign. Each ad group will be targeting a list of keywords, which will trigger your ads when users enter those keywords into the search box.
Ad groups allow you to structure your campaigns, organize your ads (e.g., by theme) and control keywords or ad associations.
Keep in mind that more isn’t the merrier when it comes to ad groups. To keep your campaigns manageable, set up a maximum of 7-10 ad groups per campaign. Each ad group should cover 10 to 20 keywords and consist of 2 to 3 ads.
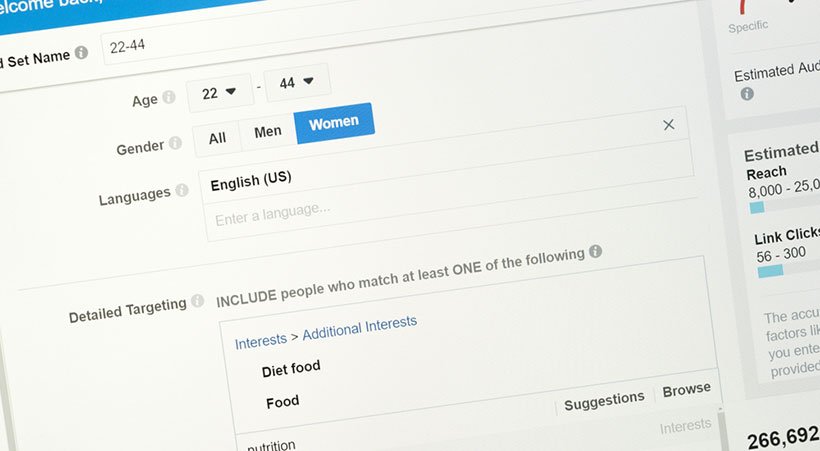
Audience
Having the right audience-message match is the key to improving your CTR and conversion rate.
There are many ways to target an audience, such as:
- Life event targeting: Use this feature to target specific audiences that are more likely to make major purchases thanks to life events such as graduation, marriage and relocation.
- Affinity and custom affinity audience: Affinity audiences are placed in pre-defined “buckets” based on their interest categories. Custom affinity audience targeting allows you to take this one step further by creating a highly-tailored audience based on users’ most recent web activities.
- In-market audience: This targeting option allows you to display ads to users who have shown high purchase intent. For instance, they compared products from a specific category in their recent browsing history.
- Custom intent audience: Can’t find a pre-defined GDN audience category that meets your needs? No problem! You can create your own custom intent audience that’s most likely to be interested in your products or services.
- Auto-created intent audience: Not sure how to jump through the hoops to create a custom intent audience? You can get Google to do it for you by leveraging its wealth of user data with this option.
- Remarketing audience: Did you know that the average cart abandonment rate for eCommerce sites is 72 percent? That means almost three-quarters of people who visited your website and put products in their carts don’t complete the checkout process. (Ouch!) Remarketing ads can help you recapture some of these prospects.
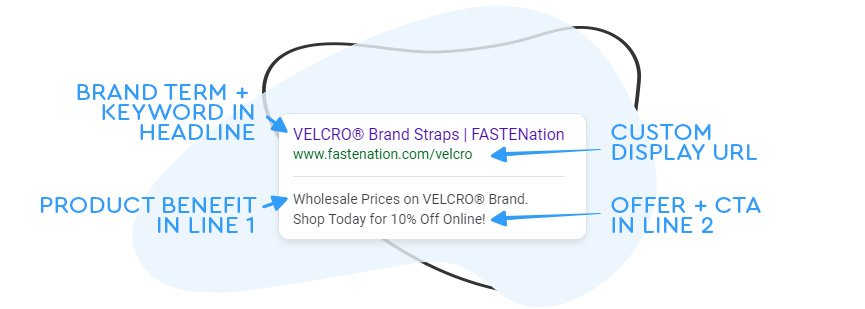
Ad Copy
Of course, we can’t forget about the nitty-gritty — what actually goes into your ads!
A text ad on the Search Network consists of a headline, a description and a URL. Here’s how to dial in your Google ad copy to maximize the impact of an ad:
- Tailor the messaging so it’s on-brand and relevant to the target audience.
- Include relevant keywords in the copy.
- Highlight the benefits of your products or services in your prospects’ language.
- Use a strong CTA that entices searchers to click through.
- Create an offer or promotion to capture attention.
- Include your prices to attract prospects with high purchase intent to get high-quality clicks.
Ad Extensions
What if you could increase the real estate your ad takes up on the search results page and bypass the ad text character limit while adding more links and information to attract the right visitors — at no extra cost?
Sound too good to be true? Google ad extensions will help you knock it out of the park.
In addition, Google has found that ad extensions can increase CTR by several percentage points, in some instances even up to 20 percent.
There are many types of ad extensions to choose from, depending on your objectives and the nature of your business:
Sitelinks Extensions
Sitelinks extension allows you to add extra links to specific pages within your site and description text under those links. Google will decide whether to show just the link or include the additional text so format the copy to show up either way.
Location Extensions
Brick-and-mortar businesses can improve their local ads with this extension by adding an address, phone number and map marker. For mobile ads, you can also include a “direction link” so searchers can easily get directions to your business.
Call Extensions
A call extension makes it easy for searchers to call your business directly from a mobile ad. Google claims that ads with a call extension get a lift in CTR by as much as 6-8 percent.
If your business can benefit from having prospects call you, adding a call extension can help generate more high-quality leads.
Callout Extensions
This extension is great for highlighting special offers or unique features of your product. You can also use it to promote same-day shipping, free delivery, discounts, etc. so you can attract searchers with high-purchase intent and increase conversion rate.
Structured Snippet Extensions
This extension shows up right below your ad copy and above the sitelinks extension.
You can choose from 12 “header” categories (e.g., styles, destinations, brands, etc.) and enter up to 10 “values” to highlight important aspects of your products or services. The structured snippet extensions can be added at the account level.
Price Extensions
This new extension format is shown under the ad copy on mobile and tablet devices as a carousel to display the prices of different products and services. It’s been found to boost CTR by as much as 400 percent, compared to text ads that don’t have any extension.
To set up a price extension, first choose a “type” (e.g., brands, products, services, etc.) and the currency. Then, add a header, description, price qualifier, price and final URL.

App Extensions
The app extension is designed for mobile and tablet ads so you can add a “download app” button to an ad, driving searchers to your app in the app store with just one click. In addition, it’ll only be shown on a device that supports the app (e.g., if your app is only available for Android, an iPhone user won’t see the extension).
Review (Seller Rating) Extensions
The review extension allows you to use data from third-party review sites on your ad. To take advantage of this feature, pull reviews on your products or services from reputable review sites so Google can verify the information and approve the ad.
These reviews and ratings can increase your ads’ CTRs and have an enormous influence on customer behaviors and purchasing decisions.
Bid Management
Through the process of bid management, you can raise and lower your keyword bids — an important factor that determines ad placement, cost-per-click and how long your budget will last.
There’s no one-size-fits-all bidding strategy, which depends on your conversion goal and CPA (cost-per-action) metrics. By understanding your sales numbers, operating costs and margins, you can calculate how much you can afford per conversion and still make a healthy profit.
To properly manage your bids, you have to assess them on a keyword-by-keyword basis.
Typically, if a keyword’s CPA is lower than your goal and the ad is appearing in a lower position, you should up your bid to increase visibility and get more clicks. On the other hand, if your keyword CPA is high and the ad is consistently appearing at the top of SERPs, you can lower the bid to drive down your CPA.
Landing Pages
Attracting traffic to your website is important, but you also need to make sure that the site is converting visitors to leads or conversions. Otherwise, you’ll be wasting a lot of money on clicks that don’t bring in revenue.
Setting up a dedicated landing page for your ads can help improve the user experience and increase conversion rate by:
- Minimizing distraction.
- Prompting visitors to take a specific action.
- Delivering content that’s consistent with the copy on the traffic source.
Here’s how to increase the effectiveness of a landing page to drive more conversion:
- Write a powerful headline that is clear, relevant and solution-oriented.
- Create original and relevant content that speaks to the audience and matches the user intent of the ad.
- State your unique selling proposition and the benefits of the product in the copy.
- Include testimonials as social proof.
- Deliver a great user experience — e.g., by optimizing page load speed, ensuring legibility on all devices and providing clear instructions.
- Use a high-quality hero image — the primary web banner image — to showcase your product.
- Include a clear call-to-action (CTA). If the page is long, put the CTA button in multiple locations to minimize scrolling.
- Ensure that the page is built on a mobile-first framework.

Last but certainly not least, split test every element by launching a new version every two to four weeks so you can keep fine-tuning the landing page and improving your conversion rate.
Analytics and Reporting
Analytics and reporting are critical if you want to improve the results of your Google Ads. There are many ways to slice and dice the information so the key is to first identify a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that are in alignment with your business objectives. That way, you can review the most relevant data and reports.
Common Metrics
Here are the most-used metrics in Google Ads:
- Click-through-rate (CTR): the rate at which an ad is clicked as a percentage of the total number of people who have seen your ad.
- Impressions: the number of searchers who have seen your ad.
- Conversions: the number of users who take a specific action (e.g., sign up for your newsletter, download an app, make a purchase) after they click through an ad.
- Cost-per-click (CPC): the amount you pay for each click.
- Cost-per-conversion/Cost-per-action (CPA): the total amount you pay divided by the number of conversions.
Conversion Tracking
In order to obtain accurate metrics for your analytics and reporting, make sure you’re tracking the conversions properly.
The process for setting up tracking differs based on the type of conversion you want to track. The first step is to identify the conversion source and the action you want searchers to take.
Examples of conversion sources include:
- Websites (e.g., making a purchase, signing up for newsletter)
- Apps (e.g., installation, in-app purchase)
- Phones (e.g., placing a call via the number listed on an ad)
- Imports/Offline conversion (e.g., visiting your store in person)
Common Reports
There are many kinds of reports to help you understand your metrics and spot important trends. Here are a few useful ones:
- Search Query Report: shows the actual search terms that trigger the display of your ads so you can understand how users are searching for your type of products or services.
- Placement Report: provides detailed site-level performance metrics on your GDN ads.
- Auction Insights Report: shows how your ads’ performance measures up to other advertisers who are participating in the same auctions.
- Segmentation Report: displays metrics from a selected segment (e.g., by device type, match type, etc.) so you can drill down for in-depth insights.
Conclusion
Google is constantly improving its advertising platform and introducing more features designed to help you gain better insights, deliver a more user-friendly experience and yield better results.
Besides learning about the latest updates, you should also pay attention to any change in your metrics when a new feature is introduced. That way, you can better understand the preferences and behaviors of your audience and customers.




Responses